CSS
Certainly! CSS, or Cascading Style Sheets, is a stylesheet language used for describing the presentation and formatting of a document written in HTML or XML. The primary purpose of CSS is to separate the structure and content of a web page (defined in HTML) from its visual presentation, allowing developers to control the appearance of elements on the page.
Core Features and Concepts of CSS:
-
Selectors:
- Selectors are patterns that match HTML elements. They are used to target specific elements on a web page and apply styles to them.
/* Example selector targeting all paragraphs */ p { color: blue; } -
Properties:
- Properties are the visual characteristics that you can apply to the selected elements. They define things like color, size, font, and spacing.
/* Example property setting the color of text to red */ color: red; -
Values:
- Values are assigned to properties and define how the property should be applied. For example,
redor12pxare values for thecolorandfont-sizeproperties.
/* Example value setting the font size to 16 pixels */ font-size: 16px; - Values are assigned to properties and define how the property should be applied. For example,
-
Selectors and Declarations:
- CSS rules consist of selectors and declarations. Selectors target elements, and declarations set the style rules for those elements.
/* Example CSS rule with selector and declaration */ p { color: blue; font-size: 14px; } -
Box Model:
- The box model is a fundamental concept in CSS that describes how elements are rendered in terms of content, padding, border, and margin.
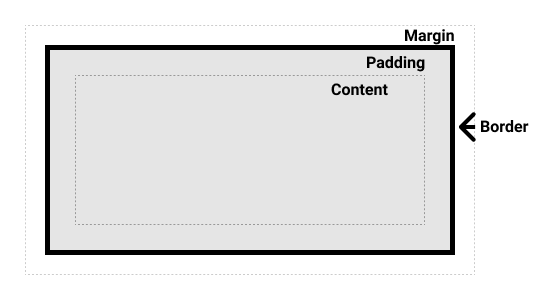
-
Cascading:
- CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets, which refers to the cascading nature of style rules. Multiple style sheets can be applied to a document, and the styles are resolved based on specificity and source order.
-
Responsive Design:
- CSS enables developers to create responsive designs that adapt to different screen sizes and devices. Media queries are commonly used to apply styles based on the characteristics of the device.
/* Example media query for responsiveness */ @media screen and (max-width: 600px) { body { font-size: 14px; } }
How CSS is Used in Web Development:
-
Linking Stylesheets:
- CSS can be included in HTML documents using the
<link>element or through inline styles using the<style>element.
<!-- Linking an external stylesheet --> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css" /> <!-- Using inline styles --> <style> body { background-color: #f0f0f0; } </style> - CSS can be included in HTML documents using the
-
Selector Types:
- CSS offers a variety of selector types, including element selectors, class selectors, ID selectors, and more, providing flexibility in styling different types of elements.
/* Example of different selector types */ h1 { color: green; } .highlight { background-color: yellow; } #main-content { border: 1px solid black; } -
Layout and Positioning:
- CSS is used to control the layout and positioning of elements on a web page. Techniques like Flexbox and Grid are commonly used for creating responsive and dynamic layouts.
/* Example of using Flexbox for layout */ .container { display: flex; justify-content: space-between; } -
Animations and Transitions:
- CSS allows for the creation of animations and transitions, enhancing the user experience. Keyframes and the
transitionproperty are commonly used for this purpose.
/* Example of a simple CSS animation */ @keyframes slide-in { from { transform: translateX(-100%); } to { transform: translateX(0); } } .slide { animation: slide-in 0.5s ease-out; } - CSS allows for the creation of animations and transitions, enhancing the user experience. Keyframes and the
-
Vendor Prefixes:
- In order to handle browser compatibility, developers may need to use vendor prefixes for certain CSS properties. This ensures that styles are applied consistently across different browsers.
/* Example of a property with vendor prefixes */ .box { -webkit-border-radius: 5px; -moz-border-radius: 5px; border-radius: 5px; }
CSS is a crucial technology in web development, providing the means to create visually appealing and responsive user interfaces. By mastering CSS, developers can control the presentation of web content, improve user experience, and ensure that their websites look and function well across different devices and browsers.
Positioning in CSS
example of the CSS code needed to apply the position property and the top, bottom, left, or right properties to adjust the position of the parent div?
Certainly! In CSS, the position property is used to control the positioning of an element, and the top, bottom, left, and right properties can be used to specify the distance an element should be offset from its normal position. Here's an example of how you can use these properties to move a parent <div> element:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Positioning Example</title>
<style>
/* Styling for demonstration purposes */
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
}
.parent-div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #3498db;
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="parent-div">Parent Div</div>
</body>
</html>In the above HTML and CSS code:
- The
bodyis styled to center its content both horizontally and vertically. - The
.parent-divclass styles the parent<div>with a background color, dimensions, and text centering.
Now, let's use the position, top, and left properties to move the .parent-div:
.parent-div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #3498db;
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
/* Positioning properties */
position: relative; /* Set position to relative */
top: 20px; /* Move 20 pixels down from its normal position */
left: 30px; /* Move 30 pixels to the right from its normal position */
}In this example:
- The
position: relative;property is applied to the.parent-div, which establishes a positioning context for its children. - The
top: 20px;property moves the.parent-div20 pixels down from its normal position. - The
left: 30px;property moves the.parent-div30 pixels to the right from its normal position.
Adjust the values of top, bottom, left, or right to reposition the element according to your requirements. It's important to note that when using position: relative;, the element is moved relative to its normal position, and the space it originally occupied is still reserved in the layout.
Preprocessor
functionality of CSS, JavaScript, and other web technologies?
A preprocessor in web development refers to a tool or program that extends the functionality of CSS, JavaScript, or other web technologies by introducing features and syntax that are not part of the native language. Preprocessors transform source code written in a preprocessed language into standard CSS, JavaScript, or other languages that browsers can understand.
Common Preprocessors:
1. CSS Preprocessors:
a. SASS (Syntactically Awesome Stylesheets):
- SASS is a CSS preprocessor that introduces features like variables, nesting, and mixins. It allows developers to write more maintainable and organized CSS code.
b. LESS:
- LESS is another CSS preprocessor with features similar to SASS, providing variables, nested rules, and mixins. It compiles into standard CSS.
c. Stylus:
- Stylus is a more flexible CSS preprocessor that allows developers to write CSS with fewer symbols and a more concise syntax. It supports both an indented syntax and a more traditional CSS syntax.
2. JavaScript Preprocessors:
a. Babel:
- While Babel is often referred to as a JavaScript compiler or transpiler, it can be considered a preprocessor for JavaScript. Babel allows developers to use the latest ECMAScript syntax and features by transforming it into an older version of JavaScript that is compatible with a broader range of browsers.
How Preprocessors Work:
-
Extended Syntax:
- Preprocessors introduce extended syntax or features that go beyond the capabilities of the standard languages. For example, CSS preprocessors introduce variables, functions, and nested rules, while JavaScript preprocessors may introduce additional syntax for asynchronous programming.
-
Compilation:
- The source code written in the preprocessed language is processed by the preprocessor, which translates it into standard CSS, JavaScript, or other languages. This process is known as compilation.
-
Browser Compatibility:
- The compiled code is what gets served to the browser. It is standard, browser-compatible code that browsers can interpret and execute.
Benefits of Using Preprocessors:
-
Code Maintainability:
- Preprocessors allow developers to write more maintainable and organized code by introducing features like variables, functions, and mixins. This can lead to more modular and readable code.
-
Productivity:
- Features such as variables and mixins in CSS preprocessors can significantly improve development productivity by reducing redundancy and enabling code reuse.
-
Cross-browser Compatibility:
- JavaScript preprocessors like Babel help ensure cross-browser compatibility by allowing developers to write code using the latest ECMAScript features while still supporting older browsers.
-
Language Enhancements:
- Preprocessors can introduce language enhancements that are not yet part of the native language. This enables developers to use advanced features and experimental syntax.
Example (SASS - CSS Preprocessor):
SCSS (Sassy CSS) Syntax:
// Variables
$primary-color: #3498db;
// Nesting
nav {
ul {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
}
li {
display: inline;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
padding: 6px 10px;
color: $primary-color;
}
}Compiled CSS:
/* Compiled CSS */
nav ul {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
}
nav li {
display: inline;
}
nav a {
text-decoration: none;
padding: 6px 10px;
color: #3498db;
}In this example, SASS is used to define variables, nesting, and other features that enhance the CSS syntax. The SASS code is then compiled into standard CSS that browsers can interpret.
Preprocessors play a significant role in modern web development by enhancing the capabilities of CSS, JavaScript, and other languages, making it easier for developers to write efficient, maintainable, and feature-rich code.